What is Forex Trading?
The word “Forex” is an abbreviation for the words “Foreign Exchange” and it’s the relative value of one currency versus another currency. The foreign Exchange market is the biggest market in the world with daily turnover (buying and selling) of up to 5 trillion dollars!
A lot of different organisations including banks, large companies, trading companies, investors and speculators all take part in the Forex market for many different reasons.
Whilst a speculator may buy and sell positions looking to make money trading Forex by fast moves in the market, large companies could be exchanging large quantities of currency for clients that need their money converted into another currency.
The Forex market is the biggest in the world and turns over up to $5 trillion per day. There is no other market in the world that even comes close to having this sort of trading volume during a 24 hour period.

The Forex market for traders is a market where they can make profit by either buying low and selling high or by selling high and buying low.
Trading Forex for retail speculative traders has not always been available, it was not until around 1996 that retail traders have been able to trade. Before this, Forex was only the domain of either large companies, or the super rich.
With the invention of new technology and the internet, Forex has opened up to all sorts of traders with the smallest traders now being able to trade only cents at a time.
Key Features of the Forex Market
- The Forex market is a 24-hour market. Currencies are traded all around the world
- Big financial centers include New York, Tokyo and London
- Forex market is a very liquid market. Liquidity is the ability to get very quickly in and out of the market at the fair market price.
- The Forex market is a fast moving market, which means that exchange rates can react very quickly to key pieces of data.
- Unlike trading shares, the Forex market is at best a zero-sum game meaning that your gains is someone else’s loss. However, the cost associated with doing business in the Forex market, like commission and spreads makes the Forex market a negative-sum game.
Where is Forex Located?
There is no central marketplace or exchange for the Forex market. Unlike stocks where each country has a processing place such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in the US or the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) in Australia, Forex is a truly global marketplace that is connected by large banks and their prices.
Because Forex has no set marketplace or exchange, there is no official daily or 24 hour closing time, although the close of the US market is generally seen worldwide as the close of the Forex market for the day and the start of the Asian session as the start of the market again.
Who Trades Forex?
The Forex market is traded by a variety of different organisations and individuals. Some of the main players in the Forex market are:
- Banks
- Trading Companies
- Large international companies
- Speculators/Retail traders
You will often hear a trader referred to as a ‘retail trader’. This is a trader who is speculating on the markets to try and make profits. The speculator looks to make a profit from small price increases. These traders will normally trade through a broker and use leverage to help them open large positions for small outlays.
Margin and leverage are covered a little more further on in section four of the course so keep reading on for more information.
Who Controls the Forex Market?
Although there is no centralized exchange for the Forex market there are lots of different structures within the Forex market that actually control the Forex prices in one way or another. There are three types of layers through where the Forex transactions is facilitated:
- Top tier layer: Is the Interbank market level where the big Banks conduct transactions with each other;
- Second tier layer: Is the EBS services which aggregates the bids and offers from different Banks, but also you can see in what size they are willing to transact at each level and other ECN platforms;
- Third tier layer: the Retail Brokers;
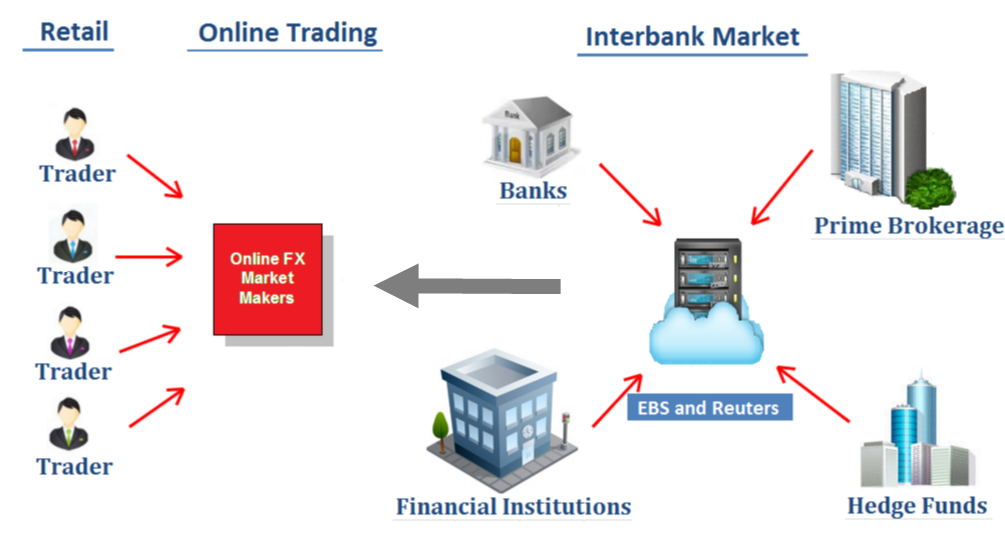
The big banks are the largest banks in the world who do actually determine the exchange rates for currencies. According to the latest data from 2015 these are the banks with the biggest Forex market share:
- CitiBank with 16.11% market share;
- Deutsche Bank with 14.54% market share;
- Barclays with 8.11% market share;
- JP Morgan with 7.65% market share;
- UBS with 7.30% market share;
These are the group of big banks that pretty much dictates the market price and in essence they are the market makers. The governments and the central banks are organisations that participates in Forex for several different reasons.Some of the major central banks around the world are the ECB (The European Central Bank), the Fed (The US Federal Reserve) and the BOJ (The Bank of Japan). The Central Banks take part in the Fx market for several reasons like:
- International trade;
- Handling Reserves;
- Intervening with currency prices;
What is Traded in the Forex Market?
When trading in the Forex market you are buying and selling currencies. Currencies are traded in what is known as pairs – more on that shortly.
The price of each currency is normally a reflection of what the market or market participants thinks of that country’s economy. Basically; if the price is rising for US dollars it is because the market thinks the US economy is strong relative to where the current price is. In other words; the price is cheap.
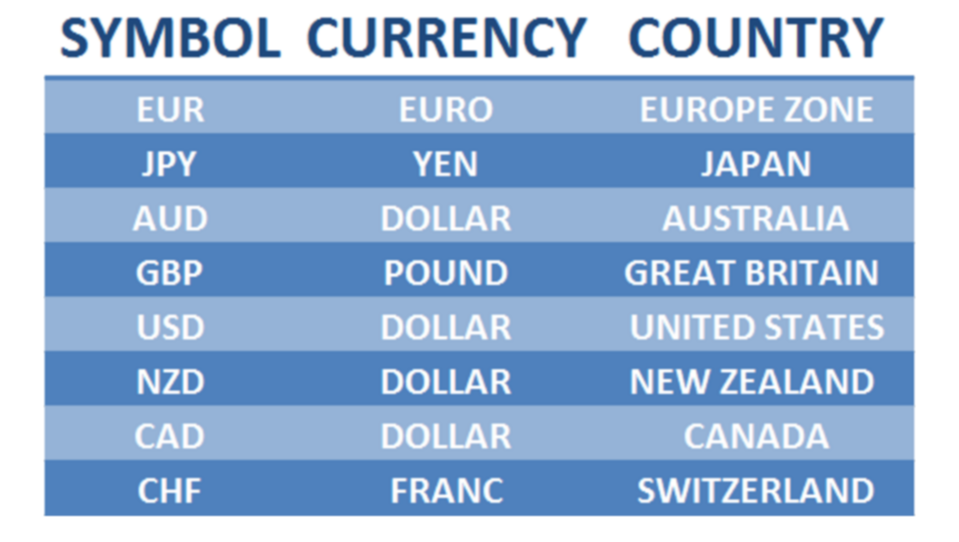
Some of the major currencies are listed below. Each currency is then given an abbreviation to make their trading symbol. For example; the Australian dollar is made into AUD. The AU is for Australia and the D stands for dollar. See below for the other main currency symbols.
Why do Exchange Rates Fluctuate?
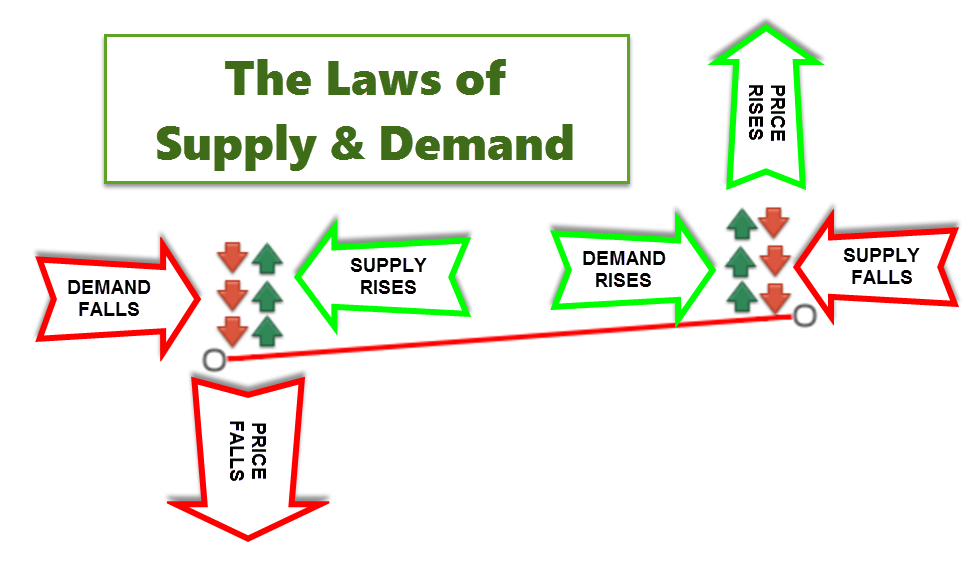
Like with every other asset classes the exchange rates of a currency pair fluctuate because of the imbalances between supply and demand levels which drives the market.
Essentially, if the demand for one particular currency pair is greater than the supply side that currency pair will rise in price, conversely, if the supply for one particular currency pair is greater than the demand side that currency pair will rise in price. The exchange rates will fall and rise until the supply and demand levels are again in equilibrium.
There are various factors that determine the exchange rate of a currency pair and since the exchange rates are relative, the macroeconomic factors have a greater degree of influencing the Forex exchange rates.
The following list represents some of the most economic factors that have an effect on the currency market:
- Central Banks monetary policy;
- Interest Rate Differential;
- Inflation;
- Current-Account Deficits;
- Public Debt;
- Political Stability and Geopolitical Stability;
How to Make Profit from Trading
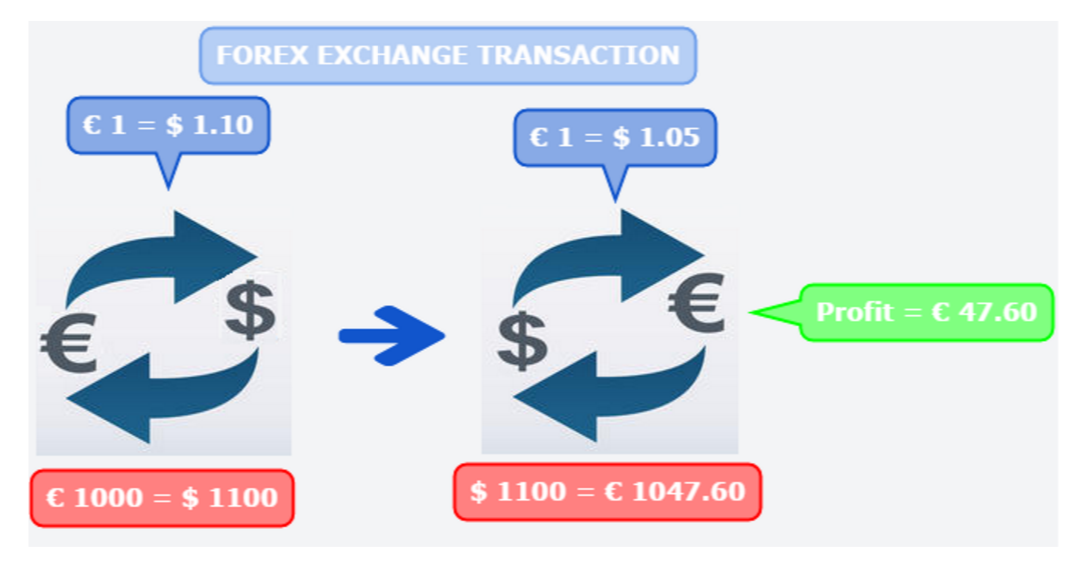
Let’s use our imagination and assume you’re a European who spends his vacation in the USA. In order to pay for the goods and services in the USA you need US Dollar and you change your 1000 euros into US Dollar at the current exchange rate of 1.10 EUR/USD which means that at the end of the transaction you end up having $1,100, but for whatever reason you don’t have the time to spend any of your money.
When you return back in Europe you still have your $1,100 but during this time the exchange rate has fluctuated from 1.10 to 1.05 EUR/USD and instead of getting just 1000 euros back you end up making a nice profit because of the new exchange rate you actually get 1047.60 euros.
You’ve just made a profit of 47.60 euros by simply holding your money in US Dollar while the EUR/USD exchange rate has depreciated in value.
In essence, this is what Forex trading is all about, we buy and sell a determined amount of one currency at a certain exchange rate and try to either make a profit if the Forex exchange rate moves in our favor or encounter a loss if the Forex exchange rate moves against us. How to trade the Forex market is essentially what we’re teaching throughout the rest of our learning tutorial lessons.

